- Liliaceae
- Lamiaceae
- Euphorbiaceae
- Leguminosae
- Zingiberaceae
- Chloranthaceae
- Campanulaceae
- Asteraceae
- Acanthaceae
- Orchidaceae
- Polygonaceae
- Ranunculaceae
- Vitaceae
- Rubiaceae
- Solanaceae
- Thymelaeaceae
- Saururaceae
- Moraceae
- Polypodiaceae
- Myrtaceae
- Araceae
- Adiantaceae
- Schisandraceae
- Amaranthaceae
- Berberidaceae
- Araliaceae
- Taxaceae
- Cucurbitaceae
- Apiaceae
- Guttiferae
- Scrophulariaceae
- Papilionaceae
- Caprifoliaceae
- Elaeagnaceae
- Apocynaceae
- Brassicaceae
- Papaveraceae
- Gentianaceae
- Paeoniaceae
- Lauraceae
- Punicaceae
- Nyssaceae
- Ephedraceae
- Gnetaceae
- Polygalaceae
- Violaceae
- Ginkgoaceae
- Cupressaceae
- Dipsacaceae
- Eucommiaceae
- Juglandaceae
- Dryopteridaceae
- Rosaceae
- Huperziaceae
- Caryophyllaceae
- Rhamnaceae
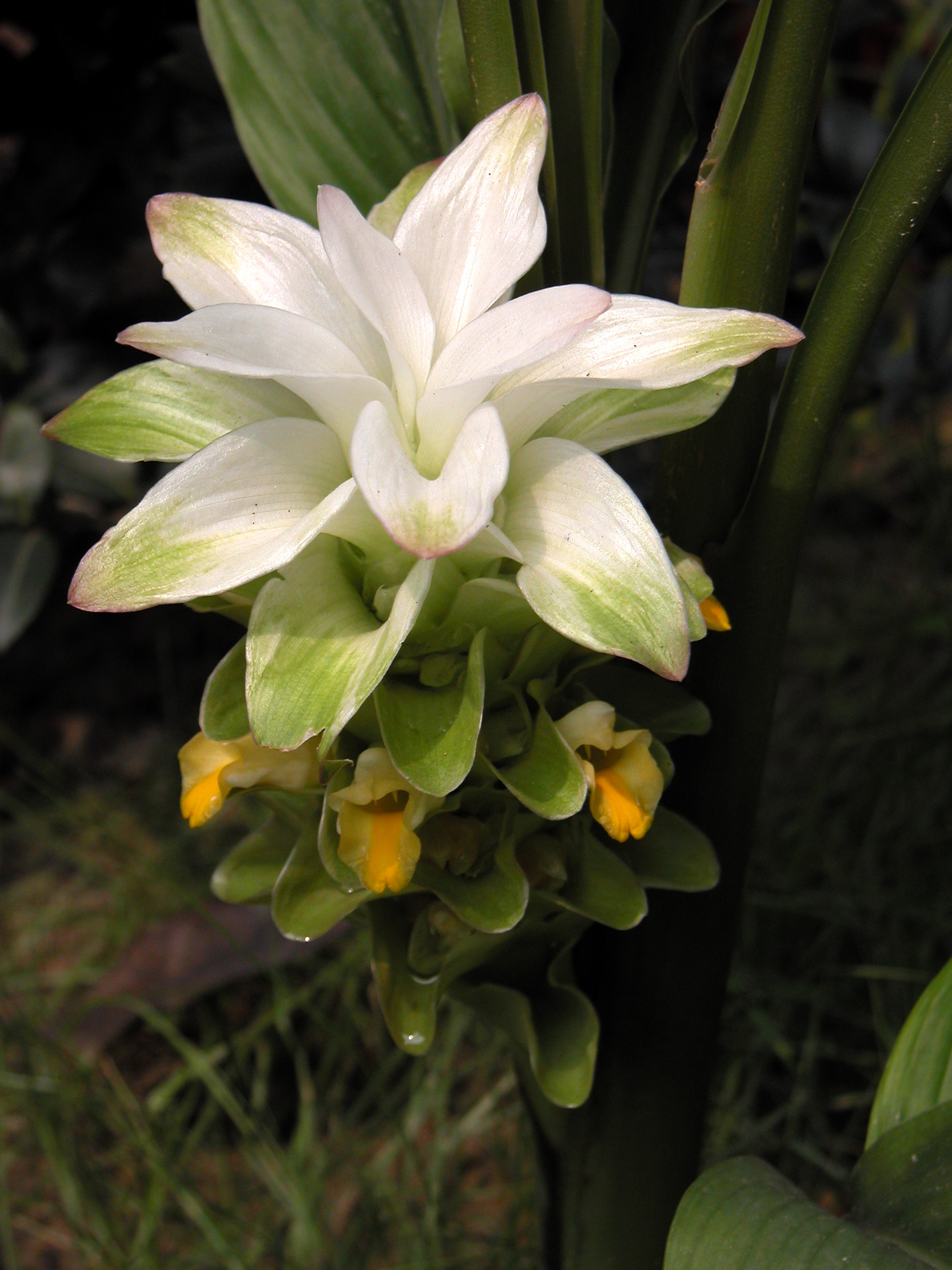

Curcuma aromatica Salisb.
- Introduction
- Download
Blast
Curcuma aromatica Salisb.The rhizomes of C. aromatic possess a reputed property to promote health conditions by arresting ageing and have immunomodulatory effects. From ancient times, it is being used as an antibiotic against various microbial infections. Historically, rhizomes are used as tonic, carminative, and externally in combinations with astringents, bitters and aromatics to bruises, in sprains and in snake-bite. They are also used for skin eruptions and infections and to improve complexion. C. aromaticahas been reported to exert various medicinal activities such as promoting blood circulation to remove blood stasis and for the treatment of cancer.
Year:2016
Institution:South China Botanical Garden, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Yunnan Agricultural University
Material: Guangzhou, China
Data link: http://www.herbal-genome.cn/index.php?m=content&c=index&a=show&catid=100&id=29
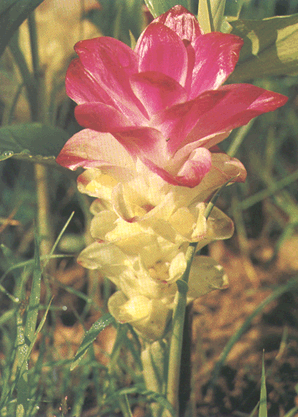
Curcuma longa L
- Introduction
- Download
Blast
Curcuma longa L. plants ca. 1 m tall. Rhizomes many branched, orange or bright yellow, cylindric, aromatic; roots tuberous at tip. The plants exhibit anti-inflammatory, anti-human immunodeficiency virus, anti-bacteria, antioxidant effects and nematocidal activities.
Year:2016
Institution:South China Botanical Garden, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Yunnan Agricultural University
Material: Guangzhou, China
Data link: http://www.herbal-genome.cn/index.php?m=content&c=index&a=show&catid=100&id=28

Curcuma zedoaria (Christm.) Rosc.
- Introduction
- Download
Blast
Curcuma zedoaria (Berg.) Rosc. (Zingiberaceae), also called Er-chu in Chinese, has long been used as a folk medicine. Traditionally, the dried rhizome of C. zedoaria is selected to make drinks or to be extracted as medicine. It has been reported that the boiling water extracts of C. zedoaria had a moderate antimutagenic activity against benzo[a]pyrene. Some hepatoprotective sesquiterpenes have been isolated from the aqueous acetone extracts of C. zedoaria rhizome. The major sesquiterpene compounds, including furanodiene, germacrone, curdione, neocurdione, curcumenol, isocurcumenol, aerugidiol, zedoarondiol, curcumenone and curcumin, were found to show potent protective effect on d-galactosamine/lipopolysaccharide-induced liver injury in mice.
Year:2016
Institution:South China Botanical Garden, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Yunnan Agricultural University
Material: Guangzhou, China
Data link: http://www.herbal-genome.cn/index.php?m=content&c=index&a=show&catid=100&id=27